BIM – IFC – ARC+
The BIM version of ARC+ (Architecture) is tailored for architects, builders, and construction professionals, offering comprehensive 3D tools alongside the capability to generate 2D drawings from 3D models. This functionality is available across all licenses except Premium 2, which exclusively offers 2D capabilities. Users can effortlessly derive facades, cross-sections, and details from the 3D model, accompanied by dimensions and textual explanations. The software also provides quick overviews of quantities and areas. ARC+ simplifies data modifications, allowing users to instantly visualize the effects of adjustments or additions.
Intended Users:
– Architects
– Contractors/Construction Companies
– Construction Consultancy Firms
– System Builders
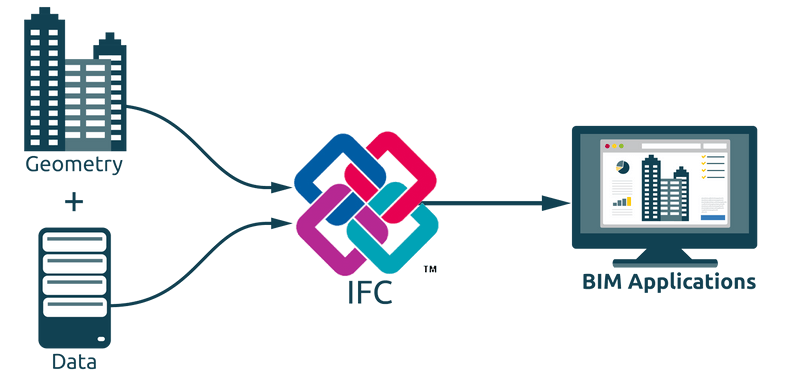
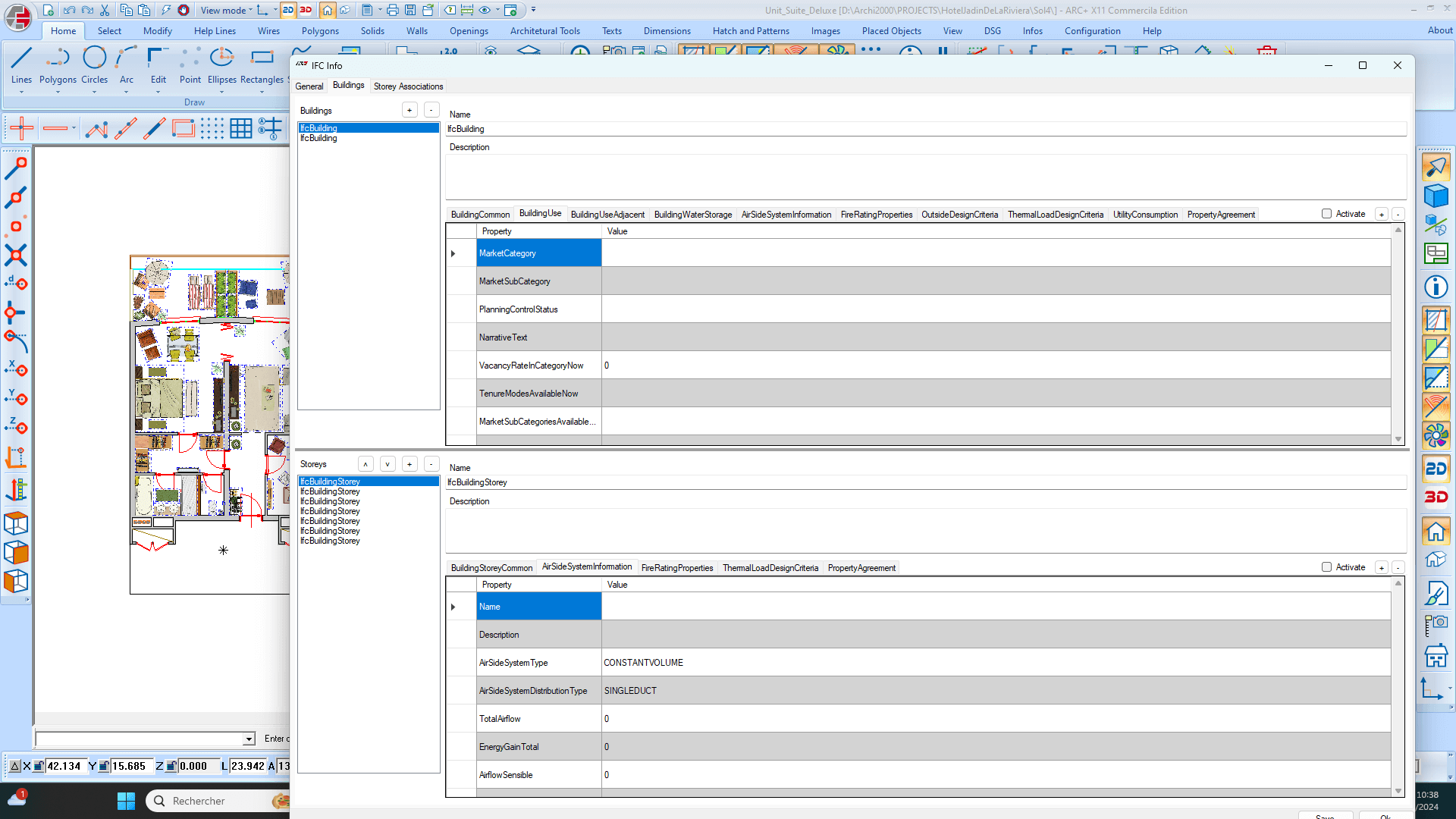
BIM, short for Building Information Modeling (or Construction Information Modeling), enables seamless communication with construction partners and clients. ARC+ facilitates the export of models to various platforms compatible with Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), the standardized language of BIM. ARC+ automatically includes essential information such as walls, frames, doors, and structural elements in its BIM models. The software provides the flexibility to classify any shape according to IFC standards when necessary. Users can save models as IFC files and expand their libraries accordingly.
Collaboration within BIM teams is streamlined through IFC’s neutral format, allowing team members to integrate their respective elements seamlessly. Construction partners can utilize the model for clash detection, quantity assessments, and energy calculations. ARC+ offers a user-friendly interface with smart selection filters, enabling users to add information selectively, optimizing efficiency during the design phase.


When IFC is necesssary?
IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) is necessary in projects that involve collaborative building information modeling (BIM) workflows, particularly when multiple stakeholders need to exchange and interact with digital building models. Specifically, IFC is essential in projects where:
1. **Interoperability** is crucial: When different software applications are used by various project participants (e.g., architects, engineers, contractors), IFC serves as a standardized format for exchanging data, ensuring compatibility and interoperability among different software platforms.
2. **Multi-disciplinary collaboration** is required: In projects where architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders work collaboratively, IFC facilitates the exchange of detailed building information across disciplines, enabling seamless coordination and integration of design, construction, and operation data.
3. **Regulatory compliance** mandates BIM standards: In regions or industries where BIM standards and regulations require the use of open data exchange formats like IFC to ensure transparency, data consistency, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. **Complex projects** with diverse building elements: In projects involving complex building structures, systems, and components, such as large-scale infrastructure projects or mixed-use developments, IFC enables the comprehensive representation and exchange of detailed building information, including geometric, spatial, and non-graphic data.
5. **International collaboration**: In projects where project stakeholders are located in different countries or regions, IFC serves as a universal language for BIM data exchange, facilitating international collaboration and communication among project participants.
In summary, IFC is necessary in projects that require seamless interoperability, multi-disciplinary collaboration, regulatory compliance, comprehensive data exchange, and international collaboration within the context of building information modeling (BIM) workflows.